Blooms Taxonomy Which Thinking Skill Is Best for Short Answer
Blooms Taxonomy defines six different levels of thinking. It is a continuum from Lower Order Thinking Skills LOTS to Higher Order Thinking Skills HOTS.
Learners who have not developed critical thinking skills skill level problem Learners who have not been challenged to go beyond remembering and understanding emotional or confidence problem To overcome these problems we need a strategy.
. According to Benjamin Bloom and his colleagues there are six levels of cognition. There can be layers of emotions and understanding in the passage. By providing a hierarchy of levels this taxonomy can assist teachers in designing performance tasks crafting questions for conferring with students and providing feedback on student work.
There are six levels of Blooms Taxonomy. I have created some lists of activities for each level of Blooms Taxonomy for your use. Language assessment through Blooms Taxonomy.
Critical Thinking Skills Blooms Taxonomy is a method created by Benjamin Bloom 1965 to categorize the levels of reasoning skills that students use for effective learning. The differentiation into categories of higher-order and lower-order skills arose later. It gives the skill of thinking in some particular orders.
Critical thinking involves evaluating the strength of ideas or concepts by asking questions about them. Remembering or recalling appropriate previously learned. Journal of Language and Linguistic Studies 14 2 76-88.
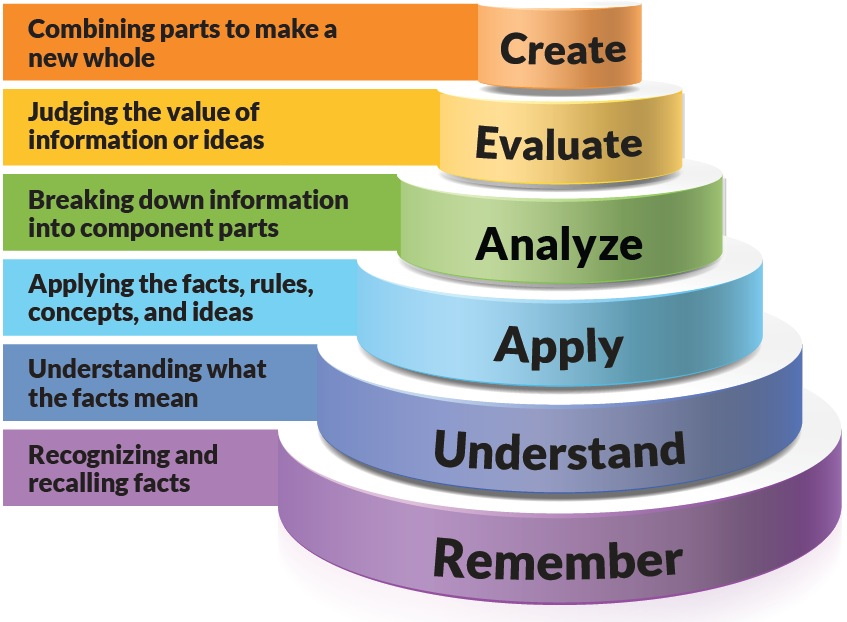
Breaking down information into component parts. Bloom labels each category with a gerund. Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis and Evaluation.
Blooms Taxonomy is a classification system that is used to define and distinguish different levels of human cognitionie thinking learning and understanding. Strategy for Using Blooms Taxonomy 1. The levels build in increasing order of difficulty from basic rote memorization to higher more difficult and sophisticated levels of critical thinking skills.
Rote memorization recognition or recall of facts. The answer lies in ongoing or formative assessment that is built into every instructional lecture not as a scale that determines success or failure but as a continuing tool for teaching. Familiarly known as Blooms Taxonomy this framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching.
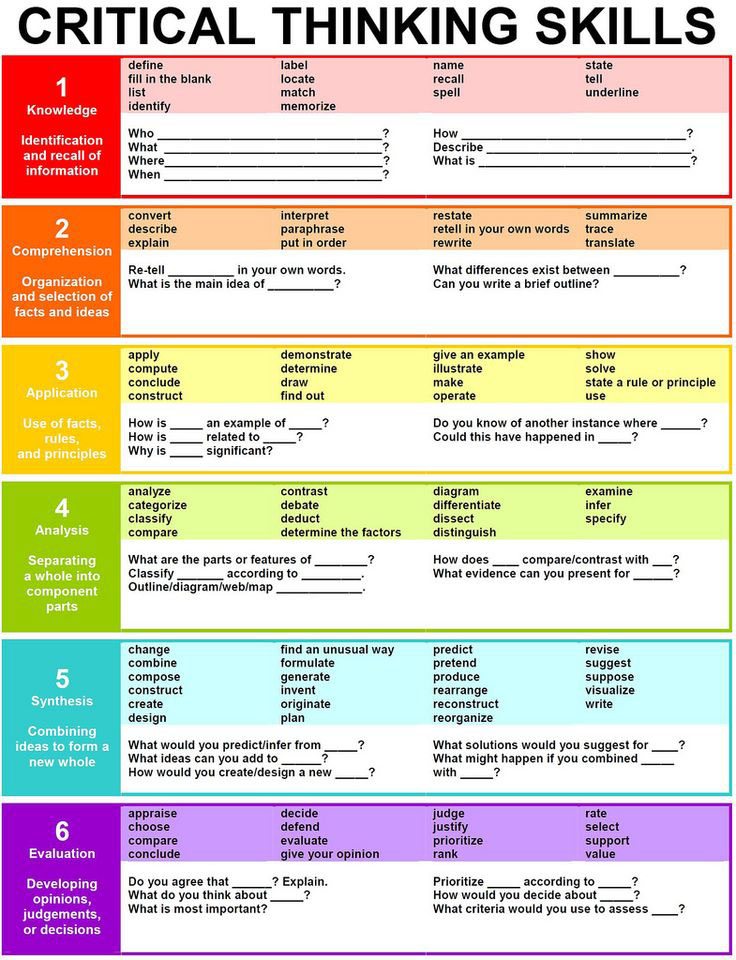
Knowledge comprehension application analysis synthesis and evaluation. Furthermore it helps in categorizing the intellectual skills into some orders of complexity and specificity. For example a test question that requires simple factual recall shows that you have knowledge of the subject.
As a teacher you should ensure that the questions you ask both in class and on written assignments and tests are pulled from all levels of the taxonomy pyramid. Blooms taxonomy contains six categories of cognitive skills ranging from lower-order skills that require less cognitive processing to higher-order skills that require deeper learning and a greater degree of cognitive processing Figure 1. A Learning domain in Blooms taxonomy dealing with growth in feelings or emotional areas Attitude.
Proposed by Benjamin Bloom as a classification tool developed to categorize learning from low level thinking to very high level thinking. Blooms Taxonomy Blooms Taxonomy provides an important framework for teachers to use to focus on higher order thinking. Submission Date19012018 Acceptance Date31052018 Abstract Benjamin Blooms taxonomy of educational objectives plays a crucial role in developing assessments that measure higher and lower level cognitive skills.
Writes a creative short story or poem or music etc Proposes a plan for an experiment Integrates learning from different areas into a plan for solving a problem Formulates a new scheme for classifying objects or events or ideas etc Categorize combine compile compose create devise design explain extend generate modify. Blooms Taxonomy divides thinking into six categories with one being the simplest level of thinking up to six which is the most complex. Most if not all teachers are taught to use Blooms Taxonomy in preparing lesson objectives for their students.
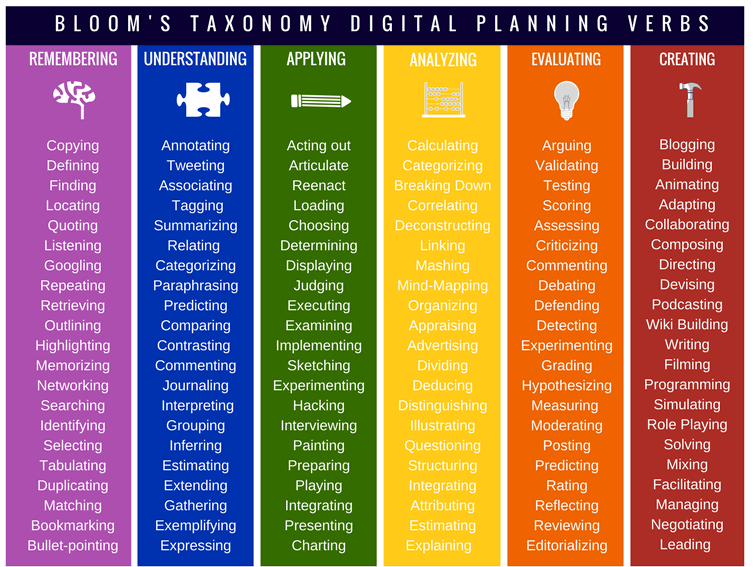
However most parents have not been taught how to use. Blooms Taxonomy is a classification system developed by educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom to categorize cognitive skills and learning behavior. Each level of skill is associated with a verb as learning is an action.
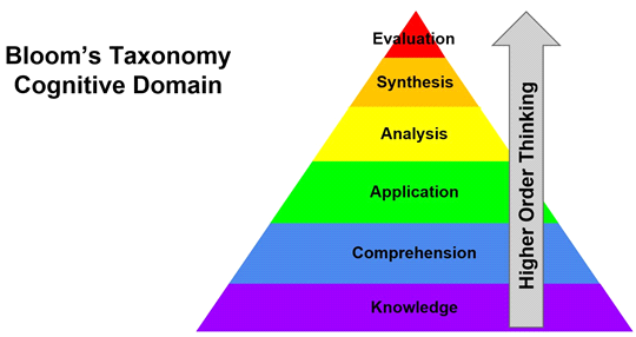
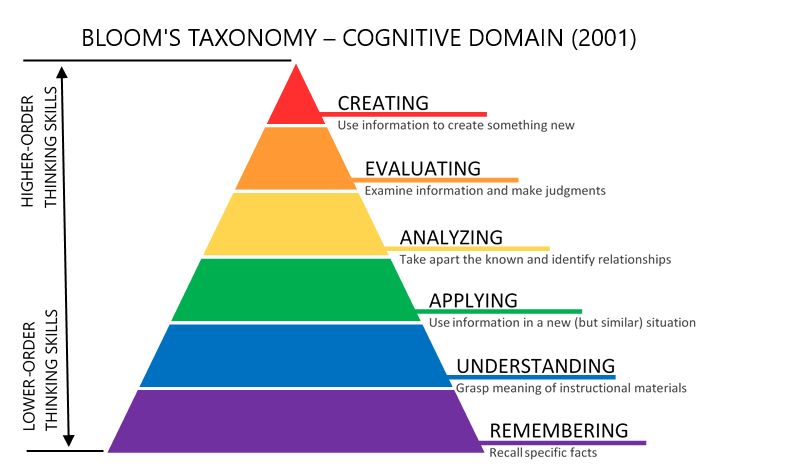
The word taxonomy simply means classifications or structures. Understanding what the facts mean. Lower order thinking skills Figure above represents the original Blooms Taxonomy which is traditionally shown in a pyramid with the lower cognitive levels at the base and higher cognitive levels at the top.
Blooms Revised Taxonomy In the 1990s a former student of Bloom Lorin Anderson revised Blooms Taxonomy and published this-Blooms Revised Taxonomy in 2001Key to this is the use of verbs rather than nouns for each of the. Blooms taxonomy is a hierarchical system that categorizes the thinking skills of students ranging from recalling information which is the. According to Watanabe-Crockett 2018 critical thinking skills is always a challenge to teach and deliver effectively to learners and the best approach is to adopt the Blooms taxonomy as the basis of learning.
Blooms Taxonomy was revised in 2001. The authors do not write the passage in one way only. Blooms Taxonomy is a three hierarchical model.
Blooms taxonomy provides a framework to describe the many kinds of thinking we need to do. The framework elaborated by Bloom and his collaborators consisted of six major categories. If you arent familiar with it Blooms Taxonomy is a hierarchy of thinking skills.
It includes six levels ranging from Remembering to Creating. Blooms Taxonomy classifies thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity. Modified Blooms taxonomy categorizations are outlined to the right of the pyramid.
Blooms revised taxonomy creates some great building blocks to get started with student achievementit helps you as an educator focus on asking. In Blooms Taxonomy there are six levels of skills ranked in order from the most basic to the most complex. Correct use of the facts rules or ideas.
Blooms Taxonomy is named after Benjamin Bloom a psychologist who in 1956 developed the classification of questioning according to six levels of higher level thinking. Creative thinking is the process of generating new ideas concepts or solutions often by adapting existing ideas or combining them in new ways to create a new solution. Being familiar with these levels can help you develop lesson activities suitable to your childs ability levels.
Make use of Blooms. Modified Blooms Taxonomy Categorizations. Bloom himself did not use these terms.

Bloom S Taxonomy The Ultimate Guide Niall Mcnulty
Bloom S Taxonomy Teaching English Tips English Efl
Critical Thinking Bloom S Taxonomy Rook Reading

Bloom S Taxonomy Bloom Et Al 1956 Download Scientific Diagram

Bloom Taxonomy Model And 21 Century Bloom S Revised Taxonomy Framework Download Scientific Diagram

How Benjamin Bloom S Taxonomy Helps Us Develop Critical Thinking Skills By Marcin Borecki The Startup Medium
36 Question Stems Framed Around Bloom S Taxonomy
Critical Thinking And Other Higher Order Thinking Skills Center For Excellence In Teaching And Learning

Bloom S Taxonomy What Is It And How It Can Be Applied Effectively To Develop Critical Thinking Skills London School Of Management Education
Using Bloom S Taxonomy To Foster Critical Thinking Adult Graduate Online Studies
100 Bloom S Taxonomy Verbs For Critical Thinking

Thinking Like A Professional Bloom S Taxonomy And Professional Download Scientific Diagram

Bloom S Taxonomy Higher Order Thinking Skills Thinking Strategies Higher Order Thinking

Bloom S Critical Thinking Cue Questions

To Own Your Learning You Must Use Higher Order Or Deeper Thinking It S About Learning

How Benjamin Bloom S Taxonomy Helps Us Develop Critical Thinking Skills By Marcin Borecki The Startup Medium


Comments
Post a Comment